How to use a colour wheel to choose your colour scheme
We all have our favourite colours and colours that we prefer to have in certain areas of our homes, but how do we best create a complete colour scheme? If we are looking for harmony or some contrast, then the best tool we can use is the colour wheel.
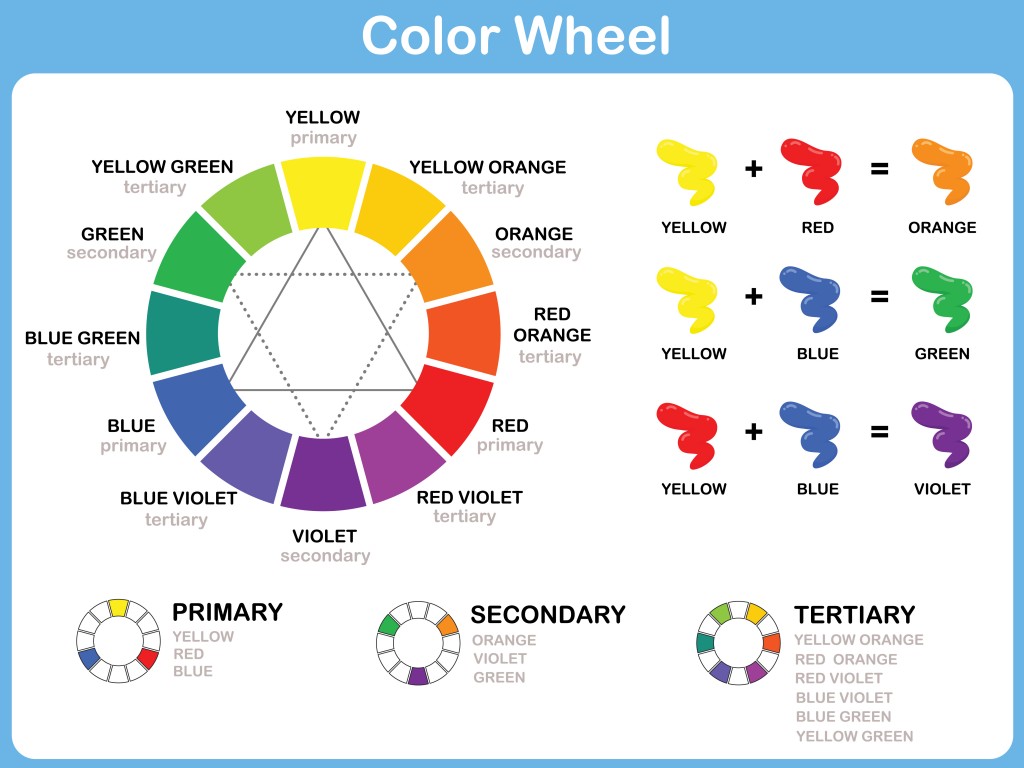
The first colour wheel was produced by Sir Isaac Newton in 1666. Since then, the basic colour wheel, which presents a sequence of pure hues arranged logically, has always been helpful.
Primary Colours
A three-part colour wheel depicting the three primary colours is a good place to start. In traditional colour theory the primary colours of
- red,
- yellow, and
- blue
can’t be formed by any combination of other colours. All other colours are derived from these three.
Secondary Colours
By adding the secondary colours of green, orange and purple, we now have a six-part wheel. The three additional colours are produced by mixing two of the primary colours together, that is
- blue + yellow = green,
- yellow + red = orange, and
- red + blue = purple.
Tertiary Colours
To form these colours we mix one primary colour with its adjacent secondary colour to produce a two-worded colour. These are
- Yellow-orange and red-orange,
- Red-purple and blue-purple, and
- Blue-green and yellow-green.
Harmony
In the context of colour, harmony is something that is pleasing to the eye. Although it is engaging, it also creates a feeling of balance. The opposite could be said to be either boring or chaotic, neither of which is very appealing, especially in a room where you are going to spend a lot of time.
Analogous Colours
There are many ideas about harmony in colour and one of them is to use analogous colours. These are any three colours which lie side by side on a 12-part colour wheel. Examples would be
- green – yellow-green – yellow, or
- yellow-green – yellow – yellow-orange, etc.
Usually one of the three colours will dominate.
Complementary Colours
These are any two colours which are directly opposite each other on a 12-part colour wheel. They could be two primary colours like red and green or two derivatives such as red-purple and yellow-green.
When creating a colour scheme with your painter and decorator, there are many possibilities. The basis of your colour scheme could be different shades of one single colour ranging from very light to very dark, or two colours you like that look appealing together. More advanced colour schemes could involve a combination of several colours based around a single colour, and this is where your colour wheel and the advice of your colour specialist painter will be very helpful.
I hope this has been of some help in deciding on your future use of colours, but when in doubt give us a call on 07976 404 742 and we can certainly assist you.





